HAProxy
When you go to HAProxy Site, the small case fonts and hardly any effort on UI make you think do they even maintain this site ? Are HAProxy days done ? But if you make effort to read along, you fumble on this line: Most users report having never ever faced any single crash and claim that HAProxy is the most solid part of their infrastructure. Finding machines with HAProxy processes being up for more than 3 years is not exceptional at all! Phew!! Flexing of highest caliber.
HAProxy is a pure backend product. No fuss, only performance. I read an article stating HAProxy served 2M req/sec. But how does HAProxy does what it does ?
As with Nginx and Caddy, HAProxy also has event-driven architecture that allows it to handle tens of thousands of connections simultaneously with minimal resources. But what separates it out is its single-purpose design. HAProxy acts as pure load-balancer and proxy. It is not a web server. Meaning that it doesn’t support file I/O operations for content serving. Its code paths are optimized for proxy operations.
Due to this single purpose design, it can focus on various depths. For ex. HAProxy has highly optimized memory management. Rather than using general purpose memory allocators like malloc/free it has implemented custom allocators optimized for their use cases. Ex
/* Simplified example of a pool allocator concept */
struct pool {
void *free_list; // List of free blocks
void *memory; // Pre-allocated memory chunk
size_t elem_size; // Size of each element
int count; // Number of elements
};
The above pool allocator benefits by elimintating fragmentation for objecs of same size. Allocation is very fast as it is just a pointer adjustment. It doesn’t need to search free lists as in general allocators.
For group of objects with similar lifetimes it uses arena allocator
/* Conceptual arena allocator */
struct arena {
void *current; // Current allocation point
void *end; // End of the arena memory
size_t size; // Total size
};
It allows fast allocation by simply incrementing a pointer and freeing entire regions at once rather than individual objects.
HAProxy uses pool-based approach for buffers. Buffers are pre-allocated fixed size buffers during startup. Used buffers are immediately returned to pool rather than freed. This eliminates overhead of frequent memory allocation/deallocation during request processing. This recycling mechanism is particularly effective because of its workload that involves many short-lived connections.
Enough of tech-talk. Let’s have some hands on with HAProxy.
Let’s simulate 3 servers: server1, server2, server3 running locally on ports 8081, 8082, 8083. They will have index.html file just indicating server number.
echo "<html><body><h1>Server 1</h1><p>This is server 1 responding.</p></body></html>" | sudo tee /var/www/server1/index.html
Unlike Nginx/Caddy , HAProxy is not a webserver. Nginx/Caddy could open port 8081 and listen on it for us. But HAProxy can’t do that. So, we will have to run python http.server on these ports
cd /var/www/server1 && sudo python3 -m http.server 8081 &
Now that 3 servers are up and running, we can load balance them with HAProxy.
frontend http_front
bind *:80
stats uri /haproxy?stats
default_backend web_servers
backend web_servers
balance roundrobin
server server1 127.0.0.1:8081 check
server server2 127.0.0.1:8082 check
server server3 127.0.0.1:8083 check
Restart HAProxy with sudo systemctl restart haproxy .
Let’s run a test to check load balancing:
for i in {1..10000}; do curl http://localhost:80; echo; done
It will send 10000 curl requests on localhost. We can see the load balancing statistics at http://localhost/haproxy?stats
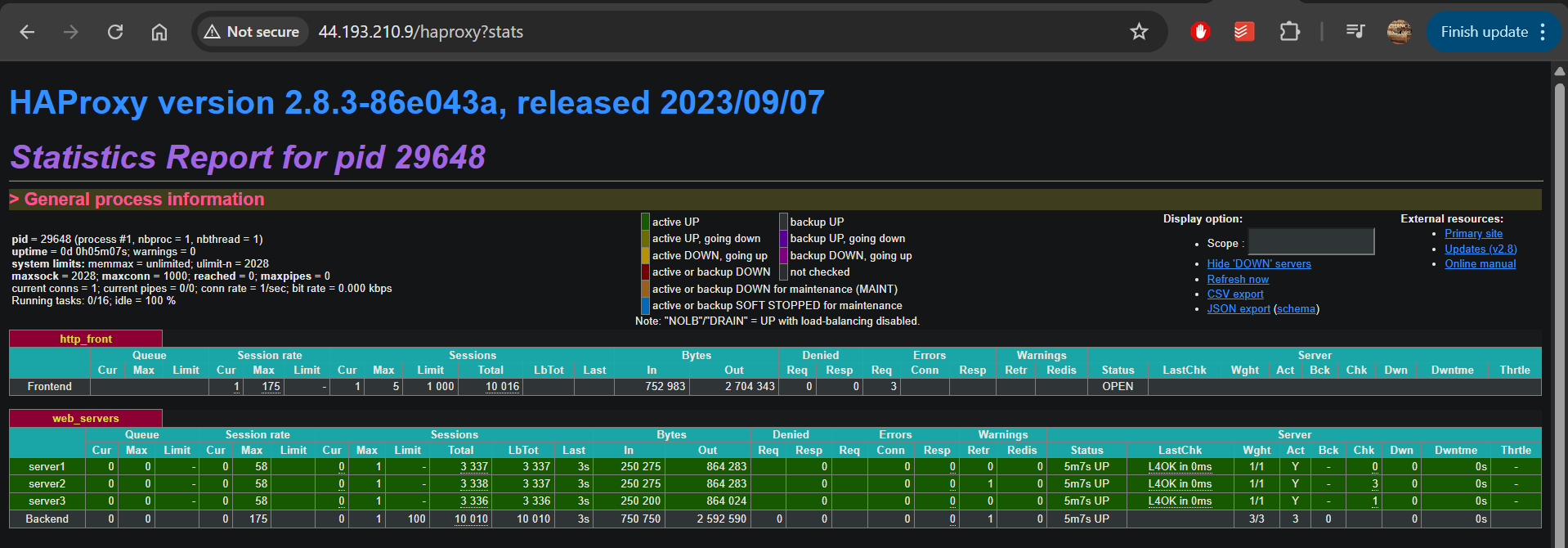
So, if everything is so green why doesn’t everyone just use HAProxy ? Well, as I mentioned above, it is a single-purpose product. While Nginx can act as both web server and load balancer, HAProxy acts only as load balancer. For faster deployments, people would use Nginx / Caddy.
While HAProxy offers very granular control over http request, in most cases people are not concerned over it. So, configuration also adds little overhead compared to Caddy.
Finally, it is slow to adopt new technologies. Meaning, it still does not support HTTP/3 while Caddy does. So, unless performance is of utmost importance, you would prefer Nginx/Caddy over HAProxy.